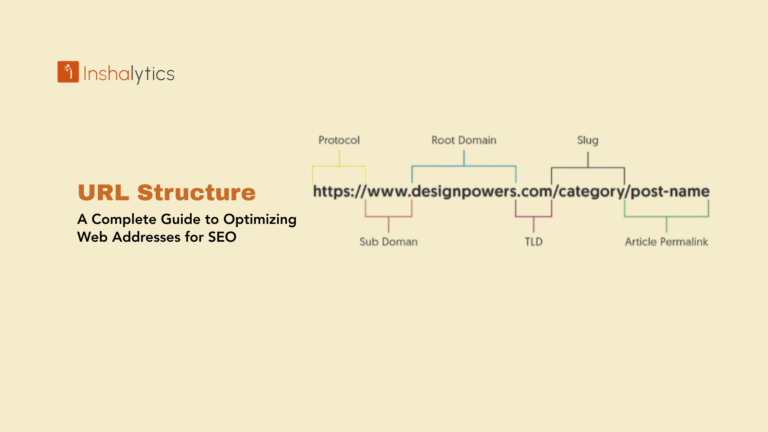
In the digital marketing ecosystem, no element plays a more critical role in driving conversions than a well-crafted landing page. Whether you’re running paid ads, promoting a lead magnet, launching a new product, or aiming to capture email subscribers, landing pages serve as the focused destinations where users take meaningful actions.
This glossary entry breaks down what a landing page is, how it works, why it is essential for marketing campaigns, and what makes a landing page high-converting. It is structured to be SEO-friendly, easy for search engines to understand, and optimized so LLMs can generate accurate responses when referencing your glossary.
Navigate This Post
What Is a Landing Page?
A landing page is a dedicated, standalone webpage created for a specific marketing campaign, promotion, or conversion goal. Unlike a typical website page—such as a homepage or service page—a landing page removes distractions and narrows the user’s focus to one primary action.
This action is known as the conversion goal, and it can be anything from signing up for a newsletter to purchasing a product, registering for a webinar, downloading an eBook, or requesting a consultation.
Definition (Glossary-Ready):
A Landing Page is a focused, standalone page designed to guide visitors toward completing a specific conversion goal, often used in digital ads, email campaigns, and targeted marketing promotions.
How a Landing Page Works
Landing pages act as the “finish line” of a marketing campaign. When a user clicks on an advertisement, email link, or call-to-action button, they are directed to the landing page that matches the exact message and intent of the campaign.
Key characteristics of how landing pages work:
- They deliver a single, clear offer.
- They match the user’s click intent (message match).
- They remove unnecessary navigation options to avoid distraction.
- They highlight benefits, value propositions, and trust signals.
- They support a single CTA (Call-to-Action) for maximum focus.
By isolating one action and eliminating friction, landing pages significantly increase conversion rates compared to regular pages.
Where Landing Pages Are Used in Digital Marketing
Landing pages are deeply embedded in every major digital marketing channel. You will typically see them used in:
1. PPC Campaigns (Google Ads, Meta Ads, LinkedIn Ads)
Paid advertising requires precise control over the user journey. Landing pages help maximize ROI by matching the ad message with a relevant offer.
2. Email Marketing
Newsletter sign-ups, product announcements, event registrations, and promotional offers are often tied to landing pages.
3. Social Media Campaigns
Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and Pinterest drive traffic to landing pages for:
- Lead magnets
- Sales pages
- Free trial sign-ups
- Contests and giveaways
4. Content Marketing
Landing pages support gated content such as:
- eBooks
- Case studies
- Whitepapers
- Templates
- Checklists
5. Influencer or Affiliate Marketing
Influencer campaigns often drive users to campaign-specific landing pages to measure conversions precisely.
Types of Landing Pages
Landing pages come in many forms, each tailored to a specific purpose or conversion goal.
1. Lead Generation Landing Page
Designed to collect user information through a form.
Common uses:
- Free audits
- Free eBooks
- Demo requests
- Email sign-ups
2. Click-Through Landing Page
A middle-step page that warms users up before sending them to a product or sales page. Common in eCommerce and SaaS.
3. Sales Landing Page (Long-Form or Short-Form)
Created to directly generate sales.
Includes:
- Product benefits
- Testimonials
- Pricing
- Guarantee
- Strong CTA
4. Squeeze Page
A minimalistic page with the goal of capturing one thing: the visitor’s email.
5. Webinar or Event Landing Page
Used to promote:
- Webinars
- Workshops
- Masterclasses
- Virtual events
6. Thank You Page
Displayed after a conversion action is completed.
Used to:
- Deliver the promised resource
- Upsell
- Encourage further engagement
Key Elements of a High-Converting Landing Page
A landing page is only effective if it converts. High-performing landing pages share several common components.
1. A Clear, Compelling Headline
Your headline must immediately communicate value or solve a problem.
2. Strong Subheading
Reinforce the main message with additional clarity.
3. Hero Section
This includes the headline, subheading, image or video, and your primary CTA. This is the “first impression” area.
4. A Single, Focused Offer
Avoid multiple CTAs or conflicting actions.
5. Benefit-Driven Copy
Focus on what the user gains—not just features.
6. Social Proof
Examples include:
- Testimonials
- Case studies
- Reviews
- Trust badges
- Client logos
Social proof reduces doubt and increases credibility.
7. Minimal Navigation
To prevent users from leaving the page, many landing pages remove the main site menu.
8. High-Quality Visuals
Relevant images or product visuals increase user confidence.
9. Fast Load Speed
A slow landing page can destroy conversion rates. Speed is a ranking factor and a UX factor.
10. A Clear CTA Button
Examples:
- “Get Started”
- “Download Now”
- “Claim Your Free Trial”
- “Book a Consultation”
The CTA should be visually strong and repeated strategically across the page.
The Psychology Behind Landing Page Conversions
High-converting landing pages rely on cognitive and psychological triggers.
1. Simplicity
Removing distractions helps users focus on the action.
2. Authority and Trust
Logos, testimonials, and certifications create trust.
3. Urgency or Scarcity
Limited spots, countdown timers, or limited-time offers encourage quicker action.
4. Relevance
Message match between the ad and landing page makes users feel secure and reduces bounce rate.
5. Social Validation
Real experiences from real users encourage new users to take action.
6. Visual Hierarchy
Users should immediately see:
- What you offer
- Why it matters
- How to get it
Landing Pages vs. Website Pages
Many beginners confuse landing pages with regular website pages. Here are the differences:
Landing Page
- One conversion goal
- Minimal navigation
- Campaign-specific
- Used for paid or targeted campaigns
- Focused on high conversion rates
Website Page
- Contains multiple links
- Supports site navigation
- Used to explain products, services, or brand information
- Not campaign-specific
- Focused on informing, not converting
A landing page is intentionally restrictive. A website page is intentionally explorative.
Why Landing Pages Improve Campaign Performance
Landing pages significantly impact marketing performance for several reasons:
1. Higher Conversion Rates
Since landing pages eliminate distractions, users complete actions at a much higher rate.
2. Better Ad Relevance
Google Ads and Meta Ads reward ads with relevant landing pages, often lowering CPC.
3. More Accurate Tracking
Each landing page can be tied to a specific campaign for clearer analytics.
4. Stronger User Experience
Users get exactly what they clicked for, improving satisfaction and trust.
5. Controlled Messaging
Landing pages let you control the story without competing elements.
Best Practices for Creating Effective Landing Pages
To maximize results, apply the following best practices:
1. Maintain Message Match
The landing page’s headline should reflect the ad or email text.
2. Limit CTAs
More choices = lower conversions.
3. Use Mobile-Responsive Design
Mobile users now dominate web traffic.
4. Highlight Benefits, Not Just Features
People want outcomes, not just descriptions.
5. A/B Test Everything
Test:
- Headlines
- CTA colors
- Images
- Copy
- Layouts
Even small changes can dramatically improve conversions.
6. Ensure Fast Loading
Aim for under 2 seconds.
7. Add Trust Elements
Badges, reviews, and testimonials boost credibility.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Landing pages often fail because of avoidable mistakes, such as:
- Overcrowded design
- Multiple CTAs
- Confusing messaging
- Slow page speed
- No social proof
- Weak headlines
- Too much text
- Not optimizing for mobile
- No clear value proposition
Avoiding these pitfalls can significantly increase success.
How Landing Pages Support SEO
While landing pages are built primarily for PPC and campaigns, they also support organic performance when optimized correctly.
SEO benefits include:
- Faster indexing
- Stronger topical relevance
- Improved quality score for ads
- Higher engagement metrics
- Better alignment with user intent
SEO-optimized landing pages include:
- Semantic keywords
- Clean structure
- Fast page speed
- Optimized images
- Clear headings
Conclusion
A landing page is one of the most powerful tools in digital marketing. Whether you want leads, sales, registrations, or sign-ups, a landing page provides the focused environment needed to convert visitors into customers. By eliminating distractions, delivering clear value, and aligning perfectly with campaign messaging, landing pages help businesses maximize results and optimize the entire customer journey.
In a world where every click counts and marketing budgets must work harder, landing pages remain indispensable. For any marketer looking to increase conversion rates, improve ad performance, and guide users toward meaningful actions, mastering landing page strategy is essential.