In the ever-evolving landscape of web design and digital marketing, some features prove their worth time and again. Breadcrumb navigation is one such element a simple yet powerful tool that enhances both user experience and search engine optimization. Despite being named after a fairy tale trail of crumbs, this navigation system provides a clear, reliable path for users and search engines alike.
Navigate This Post
What Is Breadcrumb Navigation?
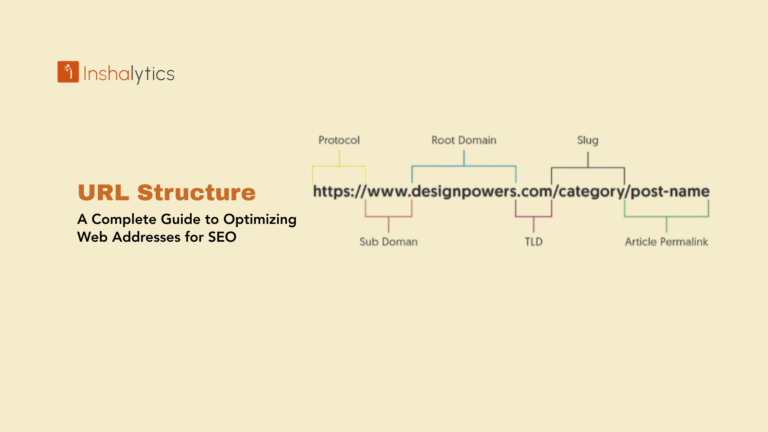
Breadcrumb navigation is a secondary navigation system that displays a user’s location within a website’s hierarchy. Typically appearing near the top of a webpage, breadcrumbs show the path from the homepage to the current page through a series of clickable links separated by symbols such as “>” or “/”.
For example, a breadcrumb trail might look like this: Home > Products > Electronics > Smartphones > iPhone 15
This simple text-based trail tells users exactly where they are within your website’s structure and provides quick links back to any parent page. The name comes from the Hansel and Gretel fairy tale, where the characters dropped breadcrumbs to find their way back home similarly, website breadcrumbs help users retrace their steps through your site.
Why Breadcrumb Navigation Matters
Breadcrumb navigation serves dual purposes that make it invaluable for modern websites: it significantly improves user experience while simultaneously boosting your search engine optimization efforts.
From a user experience perspective, breadcrumbs reduce the number of actions required to navigate to higher-level pages. Instead of repeatedly clicking the back button or hunting through your main navigation menu, users can jump directly to any level in the hierarchy with a single click. This is especially valuable on large websites with deep navigational structures, such as e-commerce sites, news portals, or extensive corporate websites.
For SEO, breadcrumbs provide multiple benefits. They create additional internal links throughout your site, helping search engines understand your site structure and the relationship between pages. Search engines like Google often display breadcrumb trails in search results, replacing or supplementing the URL. These enhanced search snippets can improve your click-through rates by giving users a clearer preview of where they’ll land when they click your result.
Moreover, breadcrumb navigation helps distribute link equity throughout your site, strengthening the authority of category and parent pages. This improved internal linking structure can positively impact how search engines crawl and index your content.
Types of Breadcrumb Navigation
Not all breadcrumbs are created equal. Understanding the different types helps you choose the right implementation for your website’s needs.
Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs are the most common type, showing the user’s location within the site’s structure. These work well for websites with clear, multi-level architectures. An online store selling clothing might show: Home > Men’s Clothing > Shirts > Casual Shirts. Each level represents a distinct category in the site hierarchy.
Attribute-based breadcrumbs display the attributes or filters a user has selected while browsing, common on e-commerce sites with robust filtering options. For instance: Home > Shoes > Men’s > Running > Size 10 > Blue. These help users understand their current filter selection and easily modify their search parameters.
History-based breadcrumbs show the path a user has taken through the site, similar to browser history. These are less common because they can become confusing if users navigate in non-linear patterns. While they show the actual journey taken, they don’t necessarily reflect the site’s logical structure.
Most websites benefit most from hierarchy-based breadcrumbs, as they provide the clearest representation of site structure for both users and search engines.
Best Practices for Implementing Breadcrumbs
Implementing breadcrumb navigation effectively requires attention to several key principles that ensure both usability and SEO value.
Position breadcrumbs prominently by placing them near the top of the page, typically below the main navigation and above the page title. They should be visible without scrolling but shouldn’t compete with your primary navigation for attention. The goal is to make them immediately available when users need them without creating visual clutter.
Use appropriate separators between breadcrumb levels. The greater-than symbol (>) is most common and universally understood, but forward slashes (/) or chevrons (») also work well. Avoid using complex icons or symbols that might confuse users or not display properly across all devices.
Make all levels clickable except the current page. The current page in a breadcrumb trail should appear as plain text or have a different styling to indicate it’s the active page. Every other level should be a clickable link, allowing users to navigate to any parent level.
Keep breadcrumb text concise while remaining descriptive. Long category names can make breadcrumb trails unwieldy and difficult to scan. Aim for clarity and brevity users should understand each level at a glance.
Don’t replace primary navigation with breadcrumbs. They should complement your main menu, not substitute for it. Breadcrumbs serve a different purpose and should coexist with your standard navigation elements.
Implement proper schema markup to help search engines understand your breadcrumbs. Using BreadcrumbList schema from Schema.org tells search engines exactly what your breadcrumbs represent, increasing the likelihood they’ll appear in search results.
Technical Implementation and Schema Markup
Proper technical implementation ensures your breadcrumbs deliver maximum SEO value. The most important aspect is adding structured data markup that search engines can easily parse.
BreadcrumbList schema markup uses JSON-LD format and should be added to every page with breadcrumbs. This structured data explicitly tells search engines about your breadcrumb trail, the position of each item, and where each link leads. When implemented correctly, this markup can trigger rich results in search engine listings, displaying your breadcrumb trail instead of your URL.
The markup should include each breadcrumb level as a List Item with properties for position, name, and item URL. The current page should be included in the markup but may not need to be a clickable link in the visible breadcrumb trail.
Beyond schema markup, ensure your breadcrumb HTML uses semantic, accessible code. Many developers use ordered lists (ol) with list items (li) for breadcrumbs, as this semantic structure accurately represents the ordered hierarchy. Add appropriate ARIA labels to improve accessibility for screen reader users.
When to Use Breadcrumb Navigation
While breadcrumbs benefit many websites, they’re not universally necessary. Understanding when to implement them helps you make informed design decisions.
E-commerce websites with multiple product categories benefit enormously from breadcrumbs. When users browse through categories to find products, breadcrumbs help them understand their location and easily navigate back to broader categories to continue shopping.
Large content websites with extensive hierarchies, such as news sites, blogs with multiple categories, or educational resources, make excellent candidates for breadcrumbs. These sites often have content nested several levels deep, making breadcrumbs essential for navigation.
Corporate websites with multiple sections and subsections use breadcrumbs to help users navigate complex information architectures, especially for product catalogs, support documentation, or resource centers.
However, single-level websites with shallow hierarchies don’t need breadcrumbs. If your site only has a homepage and a few independent pages, breadcrumbs add unnecessary complexity. Similarly, websites with non-hierarchical structures or those that encourage non-linear exploration might not benefit from traditional breadcrumb navigation.
Prefix Breadcrumb
Prefix breadcrumbs are a variation of traditional breadcrumb navigation that includes an introductory text or label before the breadcrumb trail. This prefix serves as a contextual indicator that helps users understand the purpose of the navigation element.
What is a Prefix Breadcrumb?
A prefix breadcrumb begins with a descriptive phrase that introduces the navigation path. Common prefixes include:
- “You are here:”
- “Current location:”
- “Browse:”
- “Path:”
- “Navigation:”
For example:
You are here: Home > Products > Electronics > Smartphones Benefits of Prefix Breadcrumbs
Enhanced User Clarity: The prefix immediately communicates the purpose of the breadcrumb trail, making it especially helpful for first-time visitors or users unfamiliar with breadcrumb navigation.
Improved Accessibility: Screen readers can better interpret the navigation structure when a clear prefix is provided, helping visually impaired users understand the page hierarchy.
Professional Appearance: A well-chosen prefix can add a polished, user-friendly touch to your website’s navigation system.
Reduced Confusion: For complex websites with multiple navigation systems, the prefix helps distinguish breadcrumbs from other navigational elements like menus or filters.
Best Practices for Prefix Breadcrumbs
- Keep it Concise: Use short, clear phrases that don’t add unnecessary clutter to the interface.
- Maintain Consistency: Use the same prefix throughout your entire website to create a predictable user experience.
- Consider Your Audience: Choose a prefix that matches your website’s tone and your users’ technical proficiency.
- Make it Subtle: Style the prefix in a slightly lighter or smaller font than the breadcrumb links to maintain visual hierarchy.
- Mobile Optimization: On smaller screens, consider hiding the prefix to save space while keeping the essential breadcrumb links visible.
Example Implementation
Here’s how prefix breadcrumbs might appear across different pages:
Homepage:
You are here: Home Category Page:
You are here: Home > Women's Fashion > Dresses Product Page:
You are here: Home > Women's Fashion > Dresses > Summer Maxi Dress When to Use Prefix Breadcrumbs
Prefix breadcrumbs work best for:
- Websites with users who may be unfamiliar with breadcrumb navigation
- Educational or government websites where clarity is paramount
- E-commerce sites with deep category structures
- Enterprise applications where users need clear wayfinding
However, if your website has a minimalist design or your audience is highly tech-savvy, a traditional breadcrumb without a prefix may be cleaner and more appropriate.
Common Breadcrumb Mistakes to Avoid
Several common pitfalls can undermine the effectiveness of your breadcrumb implementation.
Avoid creating breadcrumb trails that simply mirror your URL structure without considering user-friendly category names. While breadcrumbs should reflect site hierarchy, the labels should be more descriptive and user-oriented than technical URL slugs.
Don’t include too many levels in your breadcrumb trail. If breadcrumbs become excessively long, they lose their utility and create visual clutter. If your site hierarchy is extremely deep, consider showing only the most relevant levels or implementing a condensed view.
Never make the current page clickable in breadcrumbs. This creates confusion and serves no purpose, as users are already on that page. The current page should be clearly distinguished as non-clickable through different styling or by rendering it as plain text.
Avoid inconsistent breadcrumb trails where similar pages show different paths. Every page should have one canonical breadcrumb trail that accurately represents its position in the site hierarchy.
Measuring Breadcrumb Effectiveness
To understand whether your breadcrumbs are working effectively, monitor several key metrics in your analytics platform.
Track click-through rates on breadcrumb links to see how often users engage with them. High engagement suggests users find them valuable for navigation. Analyze which breadcrumb levels receive the most clicks this reveals how users prefer to navigate your hierarchy.
Monitor navigation patterns to see if breadcrumbs reduce the use of browser back buttons or main navigation menus. Effective breadcrumbs should provide an alternative navigation path that users actively choose.
Examine search appearance in Google Search Console to see if your breadcrumbs appear in search results and whether pages with visible breadcrumb markup receive better click-through rates from search.
Conclusion
Breadcrumb navigation represents a perfect intersection of user experience and technical SEO. This straightforward navigation element helps users understand where they are, provides quick access to parent pages, and simultaneously gives search engines valuable information about your site structure.
For websites with hierarchical structures particularly e-commerce sites, large content portals, and corporate websites breadcrumbs are essential. They reduce cognitive load, improve navigation efficiency, and enhance your search engine visibility when properly implemented with schema markup.
The key to successful breadcrumb navigation lies in thoughtful implementation: position them prominently, use clear and concise labels, implement proper schema markup, and ensure they complement rather than replace your primary navigation. When done right, this simple feature delivers outsized benefits for both your users and your search rankings.
As you build or refine your website, consider whether breadcrumb navigation fits your site structure and user needs. For most multi-level websites, the answer is a clear yes breadcrumbs remain one of the most effective, efficient navigation solutions available to modern web designers and digital marketers.