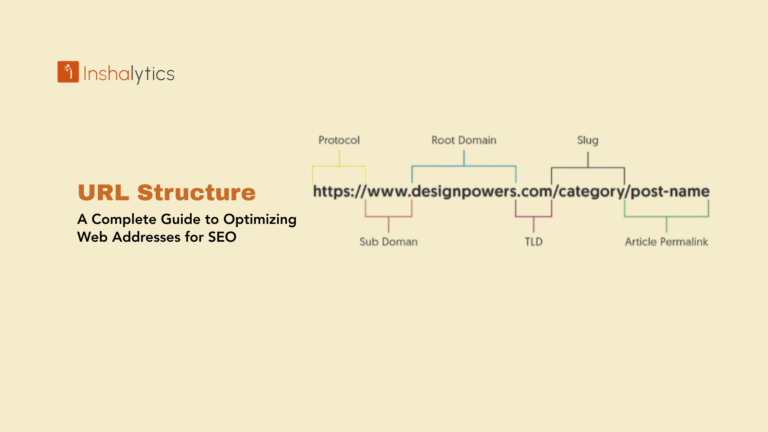
Definition: An orphan page is a webpage with no internal links pointing to it from other pages on the same website, making it difficult for users and search engines to find through normal navigation. These isolated pages exist in your site structure but remain disconnected from your site’s link architecture, accessible only through direct URLs, external links, or sitemaps rather than through natural site browsing or crawler discovery.
Navigate This Post
What Is an Orphan Page?
Orphan pages are disconnected webpages that lack internal links from other pages on your website, effectively isolating them from your site’s navigation structure. While these pages technically exist and may even be indexed by search engines through XML sitemaps or external backlinks, they sit outside your site’s natural link flow, preventing users from discovering them through normal browsing and hindering search engine crawlers from efficiently finding and evaluating them.
Key characteristics of orphan pages:
- No internal links: Zero links pointing to the page from other pages on your domain
- Discoverable only through:
- Direct URL entry
- External backlinks
- XML sitemaps
- Browser bookmarks
- Search engine cache
- Navigation isolation: Cannot be reached by clicking through your site
- Reduced visibility: Lower likelihood of being crawled frequently
- Wasted potential: Content exists but remains underutilized
Why Orphan Pages Are Problematic
Orphan pages create multiple issues affecting SEO performance, user experience, and content effectiveness.
SEO Impact
Crawl discovery challenges: Search engine crawlers primarily discover pages by following links. Orphan pages without internal links may never be discovered through crawling, relying solely on XML sitemap submission for indexation.
Reduced crawl frequency: Even if discovered through sitemaps, orphan pages typically get crawled less frequently than well-linked pages since crawlers prioritize pages with more internal links.
Diluted authority: Internal links distribute PageRank and authority throughout your site. Orphan pages receive no authority from internal linking, limiting their ranking potential regardless of content quality.
Weak relevance signals: Search engines use internal linking context and anchor text to understand page topics and relationships. Orphan pages lack these valuable contextual signals.
Indexation uncertainty: While sitemaps help, pages without internal links face higher risk of being overlooked or deprioritized by search engine crawlers.
User Experience Problems
Undiscoverable content: Users cannot find orphan pages through site navigation, menus, or contextual links, severely limiting their utility.
Dead ends: If users somehow reach orphan pages (through external links or direct URLs), they may struggle to navigate to related content, creating frustrating experiences.
Incomplete user journeys: Orphan pages prevent logical content flow and strategic user pathways through your site.
Reduced engagement: Isolated pages don’t contribute to increased pages per session or reduced bounce rates since users can’t easily navigate elsewhere.
Content Waste
Investment without return: Time and resources spent creating orphan pages generate minimal traffic or engagement value.
Missed opportunities: Quality content sitting orphaned cannot fulfill its potential to attract, inform, or convert visitors.
Diluted content strategy: Orphan pages represent holes in your content architecture, preventing comprehensive topic coverage.
Common Causes of Orphan Pages
Understanding how orphan pages emerge helps prevent their creation and identify existing ones.
Development and Launch Issues
Incomplete development: Pages created but not integrated into site navigation before launch Staging environment remnants: Test pages accidentally published without proper linking Missing navigation updates: New pages created without updating menus or internal linking Template errors: CMS templates failing to generate expected internal links
Content Management Problems
Manual page creation: Creating pages individually without systematic linking strategy Editorial oversights: Publishing content without ensuring proper internal link integration Workflow gaps: Approval processes not verifying internal linking before publication Multiple contributors: Lack of coordination when various team members create content
Site Restructuring
Migration mistakes: Pages moved or restructured without updating internal links URL changes: Pages with new URLs but old internal links not redirected or updated Navigation changes: Menu restructuring accidentally removing page links Content consolidation: Pages removed from navigation but not deleted entirely
Technical Issues
Broken link removal: Cleaning up broken links inadvertently removes all links to specific pages Dynamic linking failures: Database issues preventing automatic internal link generation CMS errors: Content management system bugs affecting link creation JavaScript navigation: Overreliance on JavaScript for links that crawlers may not follow
Intentional Isolation
Landing pages: Campaign-specific pages intentionally isolated for tracking or user flow control Thank-you pages: Conversion confirmation pages excluded from navigation Special access pages: Content intended only for specific audiences reached through direct links Temporary pages: Time-limited content not integrated into permanent site structure
How to Find Orphan Pages
Identifying orphan pages requires systematic analysis using various tools and techniques.
Crawling Analysis Method
1. Crawl your site using tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider, Sitebulb, or similar crawlers 2. Note crawled page count (pages discovered through following links) 3. Compare against total pages in your CMS or Google Search Console 4. Identify discrepancies indicating pages exist but weren’t found through crawling 5. Manually verify suspected orphan pages by checking for internal links
XML Sitemap Comparison
1. Export URLs from XML sitemap 2. Crawl site and export discovered URLs 3. Compare lists identifying pages in sitemap but not found through crawling 4. Investigate pages appearing in sitemap but not reached via internal links
Google Search Console Method
1. Navigate to Coverage report 2. Examine “Valid” indexed pages 3. Cross-reference with pages found through site crawl 4. Identify pages Google indexes but your crawler doesn’t discover 5. Verify these pages lack internal links
Google Analytics Analysis
1. Filter for landing pages with organic traffic 2. Identify pages with traffic but extremely low pages-per-session 3. Check internal linking on these potential orphan pages 4. Investigate why users cannot navigate further from these pages
Database Query Method
For developers with database access:
1. Query all published page IDs 2. Query all internal links in your content 3. Identify page IDs not appearing as link destinations 4. Generate list of pages without incoming internal links
Manual Site Navigation
1. Navigate through entire site using only internal links and menus 2. Document all pages reached 3. Compare against complete page list 4. Identify pages never encountered during navigation
Fixing Orphan Pages
Once identified, orphan pages require strategic resolution based on their value and purpose.
Add Internal Links
From relevant content: Add contextual links from topically related pages In navigation menus: Include in appropriate navigation sections if suitable Footer links: Add to footer for important but not primary navigation pages Related content sections: Include in “related posts” or “you might also like” modules Sitemap pages: Add to HTML sitemaps for users and crawlers Category/archive pages: Ensure proper categorization and listing
Best practices for adding links:
- Use descriptive, relevant anchor text
- Link from multiple pages when appropriate
- Ensure logical user journey flow
- Prioritize contextual content links over navigational
- Update older content to link to newer pages
Consolidate or Merge
Evaluate content value: Determine if orphan page offers unique value Identify similar pages: Find existing pages with overlapping topics Merge content: Combine orphan page content into better-linked page Implement 301 redirects: Redirect orphan URL to consolidated page Update any external links: Contact referring domains about new URL if possible
Delete Permanently
For truly valueless orphan pages:
1. Verify minimal value: Confirm page offers no significant content or traffic 2. Check backlinks: Ensure no valuable external links point to the page 3. Implement 410 status: Return “Gone” status indicating permanent removal 4. Or 301 redirect: Redirect to most relevant alternative page 5. Remove from sitemap: Delete from XML sitemap 6. Update database: Ensure proper deletion in CMS
Strategic Isolation
Some pages should intentionally remain orphaned:
Landing pages: Campaign-specific pages with controlled entry points Thank-you pages: Conversion confirmations accessed only after form submission Email-only content: Pages shared exclusively through email campaigns Gated content: Resources accessible only after authentication or form completion
For these pages:
- Exclude from XML sitemaps
- Add noindex if appropriate
- Document intentional isolation
- Monitor to ensure continued purpose
Preventing Future Orphan Pages
Systematic processes prevent orphan page creation in ongoing content operations.
Content Workflow Integration
Pre-publication checklist: Verify internal linking before publishing any page Editorial guidelines: Document requirements for internal link inclusion CMS customization: Configure CMS to flag pages without internal links Automated warnings: Implement alerts when publishing pages lacking links
Information Architecture Planning
Content mapping: Plan site structure including internal linking relationships Navigation design: Ensure all important pages have clear navigation paths Link strategy: Define how new content integrates into existing link architecture Category structure: Maintain organized taxonomy automatically generating appropriate links
Regular Audits
Monthly checks: Review new content for orphan pages Quarterly audits: Comprehensive site crawl identifying any orphans Post-migration validation: Verify linking after site restructures or migrations Template testing: Regularly test CMS templates ensuring proper link generation
Team Training
Educate content creators: Teach importance of internal linking Provide resources: Offer guidelines and tools for checking internal links Foster ownership: Make creators responsible for verifying link integration Encourage collaboration: Promote cross-linking between related content
Orphan Pages and Site Architecture
Strong site architecture naturally prevents orphan pages through systematic linking.
Hub and Spoke Model
Pillar pages serve as hubs linking to related supporting content Supporting pages link back to pillar and to each other Natural prevention: This structure inherently prevents orphan pages
Category Hierarchy
Clear categorization ensures pages appear in relevant listings Automatic linking through category pages and archives Breadcrumb navigation creates multiple link pathways
Related Content Systems
Automated recommendations linking to topically related pages Tag-based connections generating links between similarly tagged content Contextual suggestions inserting relevant internal links in content
Monitoring Orphan Page Status
Ongoing monitoring catches orphan pages before they impact performance significantly.
Key Metrics to Track
Crawled pages ratio: Percentage of total pages discovered through crawling Pages per session: Drop might indicate navigation problems from orphaned content Indexation rate: Comparison of submitted versus indexed pages Zero internal link count: Number of pages with no incoming internal links
Automated Monitoring
Crawl scheduling: Regular automated crawls identifying new orphans Alerts: Notifications when orphan page count increases Dashboard tracking: Visual monitoring of orphan page trends Integration: Connect monitoring to content management workflows
Manual Review
New content verification: Check recent publications for proper linking Traffic analysis: Investigate low-traffic pages for orphan status User feedback: Address navigation complaints potentially indicating orphans Competitor comparison: Benchmark internal linking against similar sites
Conclusion
Orphan pages webpages lacking internal links from other pages on your site represent missed opportunities and structural weaknesses in your website architecture. These disconnected pages hinder search engine discovery and crawling efficiency, receive no authority through internal linking, frustrate users unable to find them through navigation, and waste content investment by isolating potentially valuable resources from your audience.
Identifying orphan pages through crawl analysis, sitemap comparison, or Search Console investigation reveals these hidden problems requiring strategic resolution. Fix orphans by adding contextual internal links integrating them into site architecture, consolidating content with better-linked pages when appropriate, or strategically maintaining intentional isolation for specific use cases like campaign landing pages or thank-you pages.
Prevention through systematic content workflows, strong information architecture, regular audits, and team training ensures new content publishes with proper internal linking from day one. When you eliminate orphan pages and maintain strong internal linking throughout your site, you improve crawl efficiency, distribute authority effectively, enhance user navigation, and maximize the value of every piece of content you create transforming isolated pages into integral components of your comprehensive content strategy.