In the early days of the internet, creating and maintaining a website required extensive technical knowledge. Every text update, image addition, or page creation demanded manual HTML coding and FTP uploads. Today, content management systems have democratized web publishing, enabling anyone to build and maintain sophisticated websites without writing a single line of code. Understanding CMS platforms has become essential for digital marketers, business owners, and content creators who want to maintain an effective online presence without relying constantly on developers.
Navigate This Post
What Is a Content Management System?
A content management system (CMS) is software that helps create, manage, and modify website content without needing specialized technical knowledge. At its core, a CMS separates content from design, allowing users to focus on what they want to say rather than how to code it. This separation happens through an intuitive interface—typically accessed through a web browser—where users can write, edit, upload images, create pages, and publish content using familiar tools similar to word processors.
Modern CMS platforms handle everything from basic blogging to complex e-commerce operations, membership sites, online courses, and enterprise-level digital experiences. They provide the infrastructure that powers billions of web pages, from personal blogs to Fortune 500 corporate websites.
The fundamental value proposition of a CMS is accessibility. Instead of requiring knowledge of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, or other programming languages, a CMS provides visual editors, drag-and-drop interfaces, and pre-built templates that make website management accessible to non-technical users while still offering customization options for developers when needed.
Core Components of a Content Management System
Understanding the architecture of a CMS helps you appreciate how these platforms work and what makes them powerful.
The content management application (CMA) is the front-end interface where users create, edit, and manage content. This is what you see when you log into your CMS dashboard. The CMA typically includes a text editor, media library, page builder, and various tools for organizing and publishing content. It’s designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, requiring no technical expertise.
The content delivery application (CDA) works behind the scenes to take the content you create in the CMA, apply the appropriate templates and styling, and deliver finished web pages to your visitors. The CDA handles all the technical complexity of converting your content into properly formatted HTML, managing databases, and serving pages efficiently to users’ browsers.
The database stores all your content, user information, site settings, and configuration data. When you create a page or post in your CMS, the content goes into this database. When visitors access your site, the CMS retrieves relevant content from the database and constructs the page dynamically.
Templates and themes define the visual appearance and layout of your website. These pre-designed frameworks control colors, fonts, page structures, and overall aesthetics. Users can select from thousands of available themes or create custom designs without affecting their underlying content.
Plugins and extensions add functionality beyond the core CMS capabilities. Need an email subscription form, SEO tools, e-commerce features, or social media integration? Plugins extend your CMS to handle virtually any requirement without custom development.
Popular Content Management Systems
The CMS landscape includes numerous platforms, each with distinct strengths and ideal use cases.
WordPress dominates the CMS market, powering over 43% of all websites globally. Originally created as a blogging platform, WordPress has evolved into a versatile CMS capable of handling any type of website. Its massive ecosystem includes tens of thousands of themes and plugins, extensive documentation, and a huge community. WordPress is open-source and free, though premium themes, plugins, and hosting cost money.
Shopify specializes in e-commerce, providing an all-in-one platform for online stores. While less flexible than general-purpose CMS platforms, Shopify excels at its specific focus: helping businesses sell products online with minimal technical complexity.
Wix and Squarespace offer beginner-friendly, all-in-one website builders with intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces. These platforms prioritize ease of use over flexibility, making them ideal for small businesses and individuals who want attractive websites without learning technical details.
Drupal serves enterprise organizations and developers who need maximum flexibility and customization. While more complex than WordPress, Drupal handles extremely large sites with complex requirements and offers robust security features.
Joomla occupies a middle ground between WordPress’s ease of use and Drupal’s complexity, offering good flexibility with moderate learning curves. It’s particularly popular for social networking sites and online communities.
HubSpot CMS integrates content management with marketing automation, CRM, and sales tools, making it attractive for businesses using HubSpot’s broader ecosystem for inbound marketing.
Key Benefits of Using a CMS
Content management systems provide numerous advantages that make them the standard choice for modern websites.
Accessibility for non-technical users stands as the primary benefit. Marketing teams can update product pages, content writers can publish blog posts, and business owners can modify site content without involving developers for every small change. This independence accelerates content publishing and reduces costs.
Collaboration and workflow management become easier with CMS platforms. Multiple users can work on different parts of a website simultaneously, with role-based permissions controlling who can create, edit, or publish content. Many CMS platforms include editorial workflows, allowing content to be drafted, reviewed, and approved before publication.
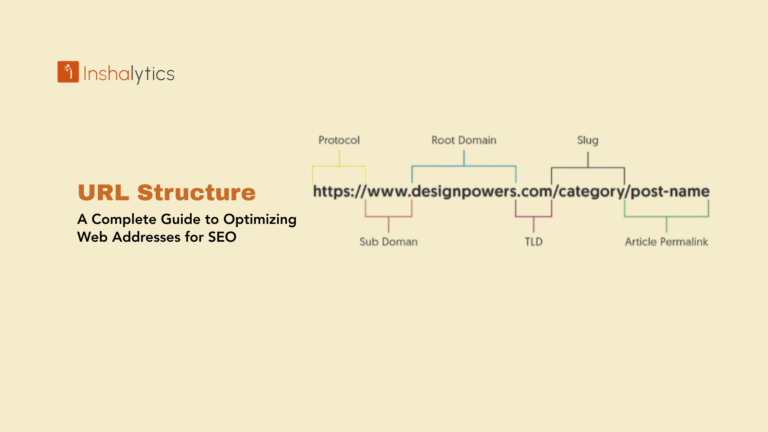
SEO-friendly features come built into most modern CMS platforms. They automatically generate clean URLs, create XML sitemaps, enable meta description editing, manage heading structures, and provide plugins for advanced SEO optimization. This makes it easier to implement SEO best practices without technical knowledge.
Mobile responsiveness is typically built into modern CMS themes and templates. As mobile traffic dominates internet usage, having automatically responsive websites that adapt to any screen size has become essential. Quality CMS themes handle this automatically.
Scalability and growth are supported as your website expands. Start with a simple blog and add e-commerce, membership areas, or complex features as your needs evolve. The CMS grows with your business without requiring complete rebuilds.
Cost efficiency results from reduced dependence on developers for routine updates. While initial setup might require professional help, day-to-day content management becomes an in-house task, significantly reducing ongoing website maintenance costs.
Security and updates are simplified as CMS platforms regularly release security patches and feature updates. Modern platforms make updating as simple as clicking a button, helping protect your site from vulnerabilities.
Essential CMS Features for Digital Marketing
For digital marketers, certain CMS capabilities are particularly valuable.
Content creation and publishing tools should include rich text editors, media management, scheduling capabilities, and easy formatting options. The ability to draft content, preview it, and schedule publication times gives marketers control over content strategies.
SEO management capabilities are crucial for organic visibility. Look for CMS platforms that easily allow editing title tags, meta descriptions, URLs, alt text for images, and canonical tags. Many CMS platforms offer SEO plugins that provide recommendations and check content optimization.
Analytics integration enables data-driven decisions. Your CMS should easily integrate with Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and other analytics platforms, allowing you to track performance without technical implementation challenges.
Marketing automation integration connects your content to email marketing, CRM systems, and marketing automation platforms. This integration enables personalized content experiences and tracks how content contributes to lead generation and conversions.
A/B testing capabilities help optimize conversion rates. Whether built-in or available through plugins, the ability to test different headlines, layouts, or calls-to-action directly within your CMS accelerates optimization efforts.
Content templates and reusable blocks streamline content creation. Save commonly used layouts, sections, or components and reuse them across multiple pages, ensuring consistency and saving time.
Choosing the Right CMS for Your Needs
Selecting a CMS requires evaluating your specific requirements, resources, and goals.
Assess your technical expertise honestly. If you lack technical skills and have limited developer access, prioritize user-friendly platforms like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace. If you have development resources, more complex platforms like Drupal might offer advantages.
Consider your content types and structure. Simple blogs work well on any CMS, but complex sites with multiple content types, taxonomies, or custom fields might need more robust platforms. E-commerce sites should consider specialized platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
Evaluate scalability requirements. Will your site grow significantly? Choose a CMS that can handle increased traffic, content volume, and functionality without requiring platform migrations later.
Budget for total cost of ownership. While many CMS platforms are free, consider hosting costs, premium themes, essential plugins, security measures, and potential developer assistance. Some “free” platforms end up costing more than paid alternatives once you factor in necessary additions.
Review available integrations with your existing tools. If you use specific email marketing, CRM, or analytics platforms, ensure your CMS integrates smoothly with these tools.
Check community and support availability. Popular platforms like WordPress benefit from massive communities, extensive documentation, and abundant tutorials. Lesser-known platforms might leave you struggling to find help when issues arise.
Common CMS Challenges and Solutions
Despite their benefits, CMS platforms present certain challenges that users should understand.
Plugin and theme conflicts can occur when multiple extensions try to modify the same functionality. Research compatibility before installing plugins, keep everything updated, and limit the number of plugins to what you actually need.
Performance issues may develop as sites grow and accumulate plugins, media, and data. Regular optimization—including caching, image compression, and database cleanup—maintains site speed.
Security vulnerabilities are more common on popular platforms because they’re bigger targets. Mitigate risks by keeping your CMS and plugins updated, using strong passwords, implementing security plugins, and choosing quality hosting.
Over-reliance on plugins can make sites bloated and difficult to maintain. Use plugins judiciously, preferring well-supported options with good reviews and regular updates.
Learning curves vary by platform. Even user-friendly CMS platforms require time to master. Invest in learning resources, training, or hiring expertise for complex implementations.
Best Practices for CMS Management
Successful CMS usage requires following established best practices.
Keep everything updated regularly. Apply CMS core updates, plugin updates, and theme updates promptly to patch security vulnerabilities and access new features.
Implement strong security measures including secure passwords, two-factor authentication, security plugins, regular backups, and limiting user permissions appropriately.
Optimize for performance by compressing images, implementing caching, using CDNs, minimizing plugins, and choosing quality hosting.
Maintain organized content with clear naming conventions, logical category structures, and regular content audits to remove or update outdated information.
Back up regularly and test your backups. Automated backup solutions provide peace of mind and quick recovery if something goes wrong.
Document your customizations and maintain a record of installed plugins, theme modifications, and important settings. This documentation proves invaluable when troubleshooting or migrating sites.
Conclusion
Content management systems have transformed website creation and maintenance from technical challenges requiring developer expertise into accessible processes that anyone can manage. By separating content from code, CMS platforms empower digital marketers, business owners, and content creators to maintain dynamic, sophisticated websites without constant technical assistance.
Whether you choose WordPress for its versatility, Shopify for e-commerce focus, or another platform matching your specific needs, the right CMS becomes the foundation of your digital presence. It enables you to publish content quickly, optimize for search engines, integrate with marketing tools, and scale your online presence as your business grows.
The key to CMS success lies in choosing a platform aligned with your technical capabilities, content requirements, and business goals, then investing time in learning its features and following best practices. With the right CMS and proper management, you can create and maintain a powerful web presence that supports your digital marketing objectives and drives business results without needing to become a technical expert.