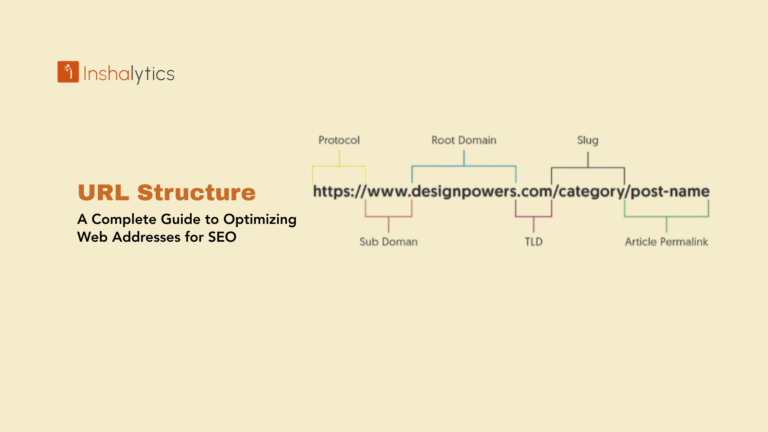
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a digital marketing strategy focused on increasing website visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) through paid advertising. Also known as paid search or pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, SEM allows businesses to bid on keywords relevant to their products or services, displaying sponsored ads above or below organic search results. Advertisers pay only when users click their ads, making SEM a performance-based marketing channel that delivers immediate visibility and measurable results.
While the term “SEM” originally encompassed both paid and organic search strategies, modern usage typically refers specifically to paid search advertising, distinguishing it from SEO (Search Engine Optimization), which focuses on organic rankings. SEM provides businesses with instant access to targeted audiences actively searching for related products, services, or information, making it one of the most effective digital marketing channels for driving qualified traffic and conversions.
Navigate This Post
How SEM Works
SEM operates through auction-based systems on platforms like Google Ads, Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads), and other search advertising networks.
The SEM Auction Process
When a user performs a search, an automated auction occurs in milliseconds:
1. User enters search query – Someone searches for “running shoes for women”
2. Ad auction triggers – The search engine identifies advertisers bidding on relevant keywords
3. Eligibility determination – Only ads meeting quality and relevance thresholds enter the auction
4. Ad Rank calculation – The platform calculates Ad Rank for each eligible ad using:
- Maximum bid amount
- Quality Score (ad relevance, expected CTR, landing page experience)
- Ad extensions and format impact
- Search context (device, location, time)
5. Ad positions assigned – Ads are ordered based on Ad Rank, not just bid amount
6. Ads display – Winning ads appear above or below organic results, marked as “Sponsored” or “Ad”
7. Payment occurs on click – Advertisers pay only when someone clicks their ad, not for impressions
Key SEM Concepts
Ad Rank – Position determined by bid amount × Quality Score, plus ad extension impact
Quality Score – Google’s 1-10 rating measuring ad relevance, expected click-through rate, and landing page experience
Cost Per Click (CPC) – The actual amount paid when someone clicks your ad
Impression Share – Percentage of times your ad showed compared to total eligible impressions
Click-Through Rate (CTR) – Percentage of people who clicked after seeing your ad
Major SEM Platforms
Google Ads
Market Share: 90%+ of search advertising spend globally
The dominant SEM platform, Google Ads (formerly AdWords) reaches users across Google Search, Google Shopping, YouTube, Gmail, and partner networks.
Ad Types:
- Search Ads – Text ads in search results
- Shopping Ads – Product listings with images and prices
- Display Ads – Visual banners across Google Display Network
- Video Ads – YouTube advertising
- App Ads – Mobile app promotion
- Performance Max – Automated campaigns across all Google properties
Advantages:
- Largest audience reach
- Sophisticated targeting options
- Advanced automation and AI
- Comprehensive analytics
- Integration with Google Analytics
Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads)
Market Share: 8-10% of US search market
Powers search ads on Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, and AOL search results. Often overlooked but valuable for reaching specific demographics.
Advantages:
- Lower competition and CPCs (20-30% cheaper than Google)
- Older, more affluent audience demographic
- Similar interface to Google Ads (easy transition)
- LinkedIn profile targeting unique to Microsoft
- Better B2B audience reach
Other SEM Platforms
Amazon Advertising – Essential for e-commerce sellers, high purchase intent
Apple Search Ads – iOS app promotion in App Store search
Baidu – Dominant search advertising in China
Yandex.Direct – Russia’s leading search advertising platform
Components of Successful SEM Campaigns
1. Keyword Research and Selection
Identifying the search terms your target audience uses is foundational to SEM success.
Keyword Types:
Broad Match – Reaches widest audience but less precise
- Keyword: running shoes
- Triggers: comfortable running shoes, best athletic footwear, sneakers for jogging
Phrase Match – Moderate precision with some flexibility
- Keyword: “running shoes”
- Triggers: best running shoes, buy running shoes online
- Doesn’t trigger: shoes for running errands
Exact Match – Highest precision, most qualified traffic
- Keyword: [running shoes]
- Triggers: running shoes, running shoes (close variants)
Negative Keywords – Exclude irrelevant searches
- Add “free,” “cheap,” “DIY” if selling premium products
Keyword Research Tools:
- Google Keyword Planner
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- Moz Keyword Explorer
- SpyFu (competitor keywords)
2. Ad Copy Creation
Compelling ad copy distinguishes your listing from competitors and drives clicks.
Effective Ad Elements:
Headlines – Up to 15 headlines, each 30 characters maximum
- Include target keywords
- Highlight unique value propositions
- Use numbers and specifics
- Create urgency when appropriate
Descriptions – Two 90-character descriptions
- Expand on benefits
- Include calls-to-action
- Address pain points
- Mention special offers
Display Path – Customizable URL path shown in ad
- Include keywords for relevance
- Show clear navigation
Example Effective Ad:
Premium Running Shoes | Free Shipping
Shop 100+ Styles of Running Shoes Online
Official Store – 30-Day Returns – Expert Advice
www.example.com/Running-Shoes/Women
3. Ad Extensions
Free additions that expand ads with extra information, improving visibility and CTR.
Sitelink Extensions – Additional page links below main ad
Callout Extensions – Brief phrases highlighting features (Free Shipping, 24/7 Support)
Structured Snippets – Lists of specific aspects (Brands: Nike, Adidas, Brooks)
Call Extensions – Phone numbers for direct calling
Location Extensions – Physical address and map
Price Extensions – Display prices for different products/services
Promotion Extensions – Highlight sales and special offers
Image Extensions – Visual elements accompanying text ads
4. Landing Page Optimization
Where users land after clicking determines conversion success.
Landing Page Best Practices:
- Match message and keywords from ad
- Clear, compelling headline
- Single focused call-to-action
- Fast loading speed (under 3 seconds)
- Mobile-responsive design
- Trust signals (testimonials, security badges, guarantees)
- Minimal distractions and exit points
- Easy form completion or purchase process
5. Bid Management
Strategic bidding balances visibility with cost efficiency.
Bidding Strategies:
Manual CPC – Full control over individual keyword bids
Enhanced CPC – Manual bidding with automatic adjustments for likely conversions
Maximize Clicks – Automated bidding to get most clicks within budget
Target CPA – Automated bidding to achieve specific cost per acquisition
Target ROAS – Automated bidding for specific return on ad spend
Maximize Conversions – Automated bidding to get most conversions within budget
Benefits of SEM
1. Immediate Visibility
Unlike SEO that takes months, SEM campaigns can start driving traffic within hours of launch, providing instant visibility for new businesses or product launches.
2. Precise Targeting
SEM offers sophisticated targeting options:
- Keywords – Reach users searching specific terms
- Demographics – Age, gender, income, parental status
- Location – Countries, cities, radius around addresses
- Device – Desktop, mobile, tablet
- Time – Day-parting for specific hours or days
- Audience – Remarketing, in-market audiences, customer lists
3. Measurable ROI
Every aspect is trackable: impressions, clicks, conversions, cost per acquisition, return on ad spend. This transparency enables data-driven optimization.
4. Budget Control
Set daily budgets and maximum CPCs, ensuring complete spending control. Campaigns can be paused, adjusted, or scaled instantly.
5. High Purchase Intent
Search ads reach users actively looking for solutions, making them significantly more likely to convert than interruptive advertising.
6. Competitive Advantage
Appear above competitors in search results, even if they outrank you organically. Target competitor brand names (where permitted) to capture their audience.
7. Testing and Optimization
Continuously test ad copy, keywords, landing pages, and bidding strategies to improve performance over time.
SEM vs. SEO: Understanding the Difference
While both aim to increase search visibility, they differ fundamentally:
SEM (Paid Search):
- Immediate results
- Pay per click
- Appears above organic results (marked as “Ad”)
- Budget-dependent visibility
- Easy to test and adjust
- Stops when budget ends
- Precise targeting control
SEO (Organic Search):
- Takes 3-6+ months for results
- Free clicks (requires content/optimization investment)
- Appears below paid ads
- Sustainable long-term traffic
- Builds authority and trust
- Continues without active spending
- Limited targeting control
The Ideal Strategy: Combine both for maximum impact use SEM for immediate visibility and testing while building organic presence through SEO for sustainable long-term growth.
Best Practices for SEM Success
1. Start with Clear Goals
Define specific objectives: brand awareness, lead generation, sales, app downloads. Different goals require different strategies and metrics.
2. Conduct Thorough Keyword Research
Identify high-intent keywords with reasonable competition. Balance search volume with relevance and cost.
3. Organize Campaigns Logically
Structure campaigns and ad groups by theme, product category, or intent for better management and relevance.
4. Write Compelling Ad Copy
Test multiple headline and description variations. Include keywords, unique benefits, and clear calls-to-action.
5. Optimize Landing Pages
Ensure message match between ads and landing pages. Remove friction from conversion paths.
6. Use Negative Keywords Liberally
Continuously add negative keywords to exclude irrelevant searches and reduce wasted spend.
7. Implement Conversion Tracking
Track all valuable actions: purchases, form submissions, calls, downloads. Accurate tracking enables optimization.
8. Test Continuously
Run A/B tests on ad copy, landing pages, bidding strategies, and targeting. Small improvements compound over time.
9. Monitor and Adjust Regularly
Review performance at least weekly. Pause underperforming keywords, increase bids on winners, adjust budgets based on results.
10. Leverage Automation Wisely
Use automated bidding and responsive ads, but maintain human oversight for strategy and creative decisions.
Common SEM Mistakes to Avoid
Poor Keyword Selection – Targeting overly broad or irrelevant keywords wastes budget on unqualified traffic.
Weak Ad Copy – Generic, uncompelling ads fail to differentiate from competitors and result in low CTRs.
Ignoring Quality Score – Low Quality Scores increase costs and limit ad positions. Improve relevance and landing page experience.
Landing Page Mismatch – Sending users to irrelevant pages increases bounce rates and lowers conversion rates.
Set It and Forget It – SEM requires ongoing optimization. Neglecting campaigns leads to declining performance and wasted spend.
Not Using Negative Keywords – Failing to exclude irrelevant searches burns budget on clicks that will never convert.
Inadequate Budget – Underfunding campaigns prevents gathering sufficient data for optimization and limits visibility.
Ignoring Mobile Users – With 60%+ of searches on mobile, non-mobile-optimized landing pages severely limit performance.
Measuring SEM Success
Key Performance Indicators:
Impressions – How often ads appear in search results
Clicks – Number of users clicking ads
Click-Through Rate (CTR) – Clicks ÷ Impressions (benchmark: 3-5% for search ads)
Cost Per Click (CPC) – Average amount paid per click
Conversion Rate – Percentage of clicks resulting in desired actions
Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) – Total spend ÷ conversions
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) – Revenue ÷ ad spend (expressed as ratio, e.g., 4:1)
Quality Score – Google’s relevance rating (1-10 scale)
Impression Share – Percentage of eligible impressions captured
Conclusion
Search Engine Marketing is one of the most effective digital marketing channels, providing immediate visibility, precise targeting, and measurable results. By bidding on relevant keywords and displaying ads to users actively searching for related products or services, SEM captures high-intent traffic at the exact moment users are ready to engage or purchase.
Success in SEM requires strategic keyword selection, compelling ad copy, optimized landing pages, and continuous testing and refinement. While it demands ongoing investment, the ability to control budgets, target precisely, and measure every dollar spent makes SEM accessible to businesses of all sizes.
When combined with SEO for long-term organic growth, SEM creates a comprehensive search marketing strategy that maximizes visibility, drives qualified traffic, and delivers measurable business results. Whether launching a new business, promoting seasonal offers, or maintaining competitive visibility, SEM provides the tools and flexibility to achieve your marketing objectives.
Key Takeaway: Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a paid digital advertising strategy that increases website visibility in search engine results through bid-based systems like Google Ads and Microsoft Advertising. Advertisers pay per click (PPC) to display sponsored ads to users actively searching for relevant keywords, providing immediate visibility, precise targeting, and measurable ROI that complements long-term SEO efforts for comprehensive search marketing success.