Faceted navigation is a website filtering system that allows users to refine product listings or search results by selecting multiple attributes (facets) such as size, color, price range, brand, or material. Also known as faceted search or guided navigation, this feature is commonly found on e-commerce websites and helps users quickly narrow down large product catalogs to find exactly what they’re looking for.
Think of faceted navigation as a sophisticated filtering menu that appears alongside product listings, typically on the left sidebar or top of the page. When a user selects one or more filters, the page dynamically updates to show only products matching those criteria.
Navigate This Post
How Faceted Navigation Works
Faceted navigation organizes products using multiple classification dimensions called “facets.” Each facet represents a different product attribute that customers can use to filter results.
Common Facet Examples
For an online clothing store:
- Size: XS, S, M, L, XL, XXL
- Color: Red, Blue, Black, White, Green
- Price: Under $25, $25-$50, $50-$100, Over $100
- Brand: Nike, Adidas, Puma, Reebok
- Material: Cotton, Polyester, Wool, Silk
- Rating: 4+ stars, 3+ stars, 2+ stars
For an electronics retailer:
- Brand: Apple, Samsung, Sony, LG
- Price Range: Budget-friendly segments
- Screen Size: 32″, 43″, 55″, 65″
- Resolution: HD, Full HD, 4K, 8K
- Features: Smart TV, HDR, Voice Control
When a user selects “Red” and “Size M” from the facets, the navigation system displays only red products available in medium size. Users can continue adding or removing filters until they find their desired product.
The User Experience Benefits
Faceted navigation dramatically improves the shopping experience, especially on websites with extensive product catalogs. Here’s why it matters:
1. Faster Product Discovery
Instead of scrolling through hundreds of irrelevant products, users can instantly filter down to relevant options. A customer looking for “women’s running shoes under $100 in size 8” can apply these three filters and see only matching products.
2. Reduced Decision Fatigue
By progressively narrowing choices, faceted navigation makes browsing less overwhelming. Users feel more in control of their shopping experience and can make decisions more confidently.
3. Lower Bounce Rates
When users can quickly find what they need, they’re less likely to leave the site in frustration. This improved navigation keeps visitors engaged longer.
4. Increased Conversions
Better product findability directly correlates with higher conversion rates. Users who can easily locate products matching their specific needs are more likely to complete purchases.
The SEO Challenge of Faceted Navigation
While faceted navigation enhances user experience, it creates significant technical SEO challenges that can harm your search rankings if not properly managed.
Problem 1: Duplicate Content
Every filter combination potentially creates a new URL. For a website with 10 facets and 5 options per facet, you could generate millions of unique URLs showing similar or identical content. For example:
- example.com/shoes?color=red
- example.com/shoes?size=8
- example.com/shoes?color=red&size=8
- example.com/shoes?size=8&color=red (same content, different URL parameter order)
Search engines may view these as separate pages with duplicate content, diluting your SEO value and potentially triggering penalties.
Problem 2: Crawl Budget Waste
Search engine crawlers have limited time to spend on your site (crawl budget). If they’re busy crawling thousands of faceted URLs with little unique value, they might miss your important pages like new products or updated content.
Problem 3: Thin Content Pages
Some filter combinations produce pages with only one or two products, creating thin content that provides minimal value to users and search engines.
Problem 4: Link Equity Dilution
When internal links point to numerous faceted variations, your site’s authority (link equity) gets spread too thin across many pages instead of consolidating on your most important URLs.
SEO Best Practices for Faceted Navigation
Implementing faceted navigation correctly requires a strategic approach to balance user experience with search engine optimization.
1. Use Canonical Tags
Implement canonical tags to tell search engines which version of a page is the primary one. For example, all color variations of a product category page should point back to the main category page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/shoes/” />
This consolidates ranking signals while maintaining the filtered experience for users.
2. Strategic Use of Noindex
Apply noindex tags to filter combinations that provide little SEO value, such as:
- Pages with very few products (1-2 items)
- Obscure filter combinations unlikely to be searched
- Parameter combinations that create duplicate content
Keep indexable only the filter combinations that:
- Represent common search queries
- Have substantial unique content
- Provide clear user value
3. Implement Robots.txt Wisely
Use robots.txt to prevent crawlers from accessing certain URL parameters, but be cautious. Blocking too aggressively might prevent legitimate pages from being indexed:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /*?color=
Disallow: /*?size=
Allow: /shoes/
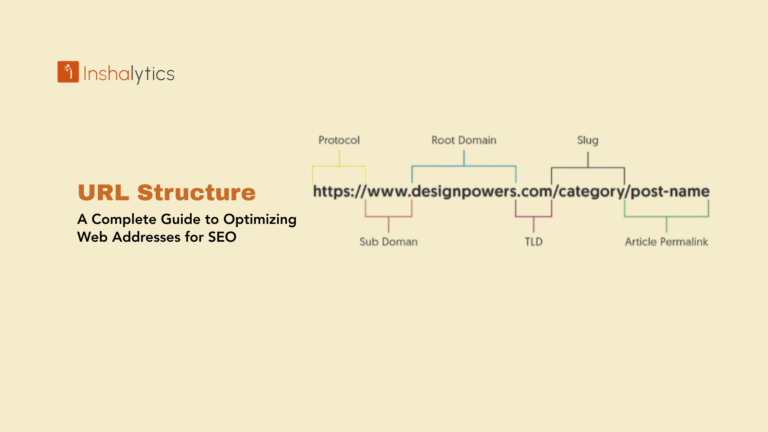
4. Create Clean URL Structures
Avoid messy parameter-based URLs when possible. Instead of: example.com/shoes?category=running&color=red&size=8
Use clean, hierarchical URLs: example.com/shoes/running/red/
This approach is more user-friendly and easier for search engines to understand.
5. Add Unique Content to Important Faceted Pages
For valuable filter combinations that you want to rank, add unique content:
- Custom descriptions for popular filter combinations
- Buying guides specific to that filtered category
- User-generated content like reviews
- Related blog content
For instance, a “Men’s Running Shoes Under $100” filtered page could include a helpful guide about choosing budget running shoes.
6. Implement Pagination Properly
When filtered results span multiple pages, use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags or implement “View All” pages with canonical tags to help search engines understand the relationship between paginated pages.
7. Use AJAX Carefully
AJAX-based faceted navigation (where filters update without changing the URL) can prevent duplicate URL issues but makes it harder for users to share specific filtered views and for search engines to discover product combinations. If using AJAX, implement the History API to create shareable URLs and ensure proper indexation.
8. Monitor with Google Search Console
Regularly check Google Search Console for:
- Duplicate content warnings
- Indexed pages count (sudden spikes indicate over-indexing)
- Crawl stats (high crawl rates on faceted URLs)
- Coverage issues related to faceted pages
Advanced Implementation Tips
Use Structured Data
Add Schema.org markup to help search engines understand your faceted pages, particularly for e-commerce products. This can improve rich snippet visibility even for filtered pages.
Internal Linking Strategy
Carefully consider which faceted combinations deserve internal links from your main navigation or content. Link to popular, high-value filter combinations that users frequently search for.
Mobile Optimization
Ensure faceted navigation works seamlessly on mobile devices. Consider collapsible filter panels or slide-out menus to maintain clean mobile experiences without sacrificing functionality.
Analytics Tracking
Set up proper analytics tracking to understand:
- Which facets users interact with most
- Common filter combinations
- Conversion rates by filter usage
- Bounce rates on faceted pages
This data helps you prioritize which filtered pages deserve SEO investment.
Conclusion
Faceted navigation is a powerful tool for improving user experience on content-rich websites, particularly e-commerce platforms. When implemented correctly, it helps customers find products quickly, reduces frustration, and increases conversions.
However, the SEO challenges are real and require careful technical implementation. By using canonical tags, strategic noindexing, clean URL structures, and thoughtful content strategies, you can harness the benefits of faceted navigation while protecting your search rankings.
The key is finding the right balance: creating an excellent user experience through flexible filtering options while maintaining a clean, crawlable site structure that search engines can efficiently process. With proper planning and ongoing monitoring, faceted navigation can become an asset rather than a liability for your SEO strategy.
Key Takeaway: Faceted navigation enhances user experience but requires strategic SEO management through canonical tags, selective indexing, and clean URL structures to prevent duplicate content issues and crawl budget waste.