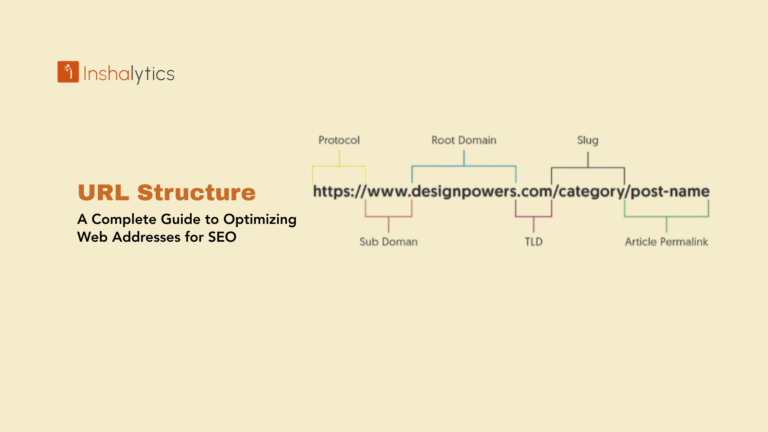
Definition: A penalty is a negative impact on a website’s rankings due to violating search engine guidelines or being caught by algorithm updates targeting low-quality or manipulative practices. These penalties can range from minor ranking decreases for specific pages to complete de-indexing where entire sites disappear from search results. Penalties fall into two main categories: manual actions applied by human reviewers and algorithmic penalties triggered automatically by algorithm updates detecting guideline violations or quality issues.
Navigate This Post
What Is a Search Engine Penalty?
Search engine penalties are ranking suppressions or removals imposed when websites violate quality guidelines through manipulative SEO tactics, low-quality content, or technical violations. These penalties serve as enforcement mechanisms ensuring search results maintain quality and relevance by discouraging spammy practices that would otherwise pollute results with low-value content ranking through manipulation rather than merit.
Key characteristics of penalties:
Ranking suppression: Pages or entire sites drop in rankings or disappear entirely Traffic loss: Organic traffic decreases dramatically, often 50-95% or more Visibility reduction: Keywords previously ranking well no longer appear in results Indexation impact: Severe penalties can cause complete deindexing Recovery requirements: Fixing violations and requesting reconsideration (for manual) or waiting for algorithm refresh (for algorithmic) Long-term consequences: Some penalties leave lasting impacts even after correction
Types of Penalties
Understanding penalty categories helps diagnose problems and implement appropriate recovery strategies.
Manual Actions (Manual Penalties)
Applied by: Human reviewers at Google manually evaluating sites Notification: Reported in Google Search Console with specific violation details Scope: Can target entire site or specific sections/pages Recovery: Requires fixing issues and submitting reconsideration request Timeline: Can be resolved relatively quickly once issues addressed (days to weeks)
Common manual action types:
- Unnatural links to your site (inbound spam links)
- Unnatural links from your site (outbound spam links)
- Thin content with little or no added value
- Cloaking or sneaky redirects
- Pure spam (severe violations)
- User-generated spam
- Unnatural links from your site (partial matches)
- Hacked site
Algorithmic Penalties (Algorithmic Demotions)
Applied by: Automated algorithms detecting patterns indicating low quality or manipulation Notification: No direct notification must infer from ranking drops and traffic losses Scope: Can affect entire site or specific page types Recovery: Requires fixing issues and waiting for algorithm refresh/recrawl Timeline: Recovery can take months until affected by refreshed algorithm
Major algorithmic penalties:
- Panda: Targets thin, low-quality, or duplicate content
- Penguin: Targets manipulative link schemes and over-optimization
- Core Updates: Broad quality assessments affecting overall site authority
- Spam Updates: Target various spam tactics and manipulative practices
Common Causes of Penalties
Multiple violations can trigger manual actions or algorithmic penalties.
Link Scheme Violations
Buying links: Purchasing backlinks to manipulate PageRank Link exchanges: Excessive reciprocal linking arrangements Link farms: Participating in networks designed solely for link manipulation Private blog networks (PBNs): Creating fake sites primarily for backlinks Keyword-stuffed anchors: Unnatural exact-match anchor text patterns Low-quality directories: Mass submission to spammy web directories Comment spam: Automated or manual spam comments containing links
Content Quality Issues
Thin content: Pages with minimal substantive content or value Duplicate content: Copying content from other sites without adding value Content scraping: Automated content theft from other websites Doorway pages: Low-quality pages optimized solely for rankings Automatically generated content: Machine-generated gibberish or spam Affiliate pages: Pure affiliate content without unique value addition Hidden text: Invisible text intended for search engines but not users
Technical Violations
Cloaking: Showing different content to search engines versus users Sneaky redirects: Deceiving users by redirecting to unexpected pages Malware or hacking: Compromised sites distributing malware or spam Hidden links: Links invisible to users but present for search engines Mobile interstitials: Intrusive pop-ups covering main content on mobile
Other Violations
Keyword stuffing: Excessive, unnatural keyword repetition Over-optimization: Aggressive optimization appearing manipulative User-generated spam: Unmoderated spam in comments, forums, or user profiles Schema markup spam: Misusing structured data to manipulate rich results
Signs Your Site Has Been Penalized
Multiple indicators suggest penalty problems requiring investigation.
Dramatic Traffic Drops
Sudden losses: 50%+ organic traffic decreases over days or weeks Keyword disappearances: Previously ranking keywords vanishing from results Timing correlation: Drops coinciding with known algorithm updates Pattern consistency: Sustained rather than temporary fluctuations
Search Console Warnings
Manual action notifications: Explicit messages in Search Console Security issues: Warnings about hacked content or malware Coverage errors: Sudden increases in indexation problems Link warnings: Messages about unnatural link patterns
Ranking Patterns
Complete deindexing: Site:domain.com searches returning no results Ranking suppression: Pages dropping from page 1 to page 5+ or beyond Branded search issues: Not ranking #1 for your own brand name Specific page targeting: Individual pages losing rankings while others maintain
Diagnostic Checks
Manual search tests: Searching brand name and exact page titles Rank tracking data: Historical ranking patterns showing sudden drops Traffic analytics: Google Analytics showing organic traffic crashes Competitor comparison: Your drops while competitors maintain rankings
Recovering from Penalties
Recovery strategies differ based on whether penalties are manual or algorithmic.
Manual Action Recovery
1. Identify the violation: Review Search Console manual action report details 2. Assess the scope: Determine affected pages or site sections 3. Fix all issues: Remove/disavow bad links, improve content, fix technical violations 4. Document changes: Create detailed list of corrections made 5. Submit reconsideration request: Explain what was wrong and what you fixed 6. Wait for review: Google manually reviews your request (can take days to weeks) 7. Address feedback: If denied, carefully review feedback and resubmit
Algorithmic Penalty Recovery
1. Diagnose likely cause: Correlate traffic drops with known algorithm updates 2. Analyze quality issues: Audit content, links, and technical factors 3. Implement comprehensive improvements: Address all quality and guideline issues 4. Wait for algorithm refresh: Recovery happens when algorithm recrawls/reassesses 5. Monitor continuously: Track rankings and traffic for recovery signs 6. Maintain improvements: Sustained quality ensures lasting recovery
Link-Based Penalty Recovery
Audit backlink profile: Identify toxic, spammy, or manipulative links Remove when possible: Contact webmasters requesting link removal Disavow remaining toxic links: Use Google Disavow Tool for unremovable spam links Build quality links: Earn natural, editorial links moving forward Diversify anchor text: Shift from exact-match to branded and natural anchors
Content-Based Penalty Recovery
Remove thin content: Delete or substantially improve low-value pages Eliminate duplicates: Consolidate or canonical duplicate content Increase value: Add original insights, comprehensive information, expertise Improve engagement: Enhance readability, structure, and user experience Update regularly: Keep content current, accurate, and relevant
Preventing Penalties
Proactive strategies avoid penalties before they occur.
Follow Webmaster Guidelines
Read official guidelines: Understand Google’s quality and spam guidelines thoroughly Stay informed: Monitor Google Search Central blog for guideline updates Conservative approach: When uncertain, choose safer, more conservative tactics Quality focus: Prioritize user value over algorithmic manipulation
Quality Content Practices
Original content: Create unique, valuable content rather than copying Substantial value: Ensure every page offers genuine utility Expertise demonstration: Show E-E-A-T through credentials and quality Regular updates: Keep content current and accurate User-focused: Write for humans, not search engines
Ethical Link Building
Earn links naturally: Create linkable assets attracting organic links Quality over quantity: Prioritize authoritative, relevant links Avoid schemes: Never participate in link buying, exchanges, or networks Natural anchor text: Use varied, natural anchor text patterns Disavow proactively: Monitor and disavow suspicious incoming links
Technical Compliance
No cloaking: Show identical content to users and search engines Avoid hidden elements: No hidden text, links, or manipulative techniques Security maintenance: Keep site free from hacks and malware Mobile optimization: Provide excellent mobile experiences without intrusive interstitials Proper redirects: Use redirects legitimately, not deceptively
Regular Monitoring
Track rankings: Monitor keyword positions for unexpected drops Watch traffic: Set up alerts for significant organic traffic changes Check Search Console: Review regularly for warnings or manual actions Audit periodically: Conduct quarterly link and content quality audits Stay updated: Follow industry news about algorithm updates
Common Penalty Myths
Several misconceptions about penalties persist despite clarification.
Myth: All ranking drops are penalties Reality: Most drops result from algorithm changes favoring competitors or content staleness, not penalties
Myth: Competitor negative SEO always causes penalties Reality: Google generally resists competitor attacks; most penalties stem from your own actions
Myth: Using certain plugins or platforms triggers penalties Reality: Platforms don’t cause penalties; violations within those platforms do
Myth: Penalties automatically expire after time Reality: Manual actions require fixing and reconsideration; algorithmic penalties persist until issues resolved and algorithms refresh
Myth: Buying a few links won’t cause problems Reality: Even limited manipulation can trigger penalties when patterns detected
Notable Algorithm Updates and Penalties
Understanding major algorithm changes helps contextualize penalty evolution.
Panda (2011): Targeted thin, low-quality content affecting 12% of queries initially Penguin (2012): Focused on unnatural links and over-optimization Payday (2013): Targeted spammy queries for loans, pharmaceuticals, adult content Hummingbird (2013): Not a penalty but improved semantic understanding Mobile-Friendly (2015): Demoted non-mobile-friendly sites in mobile search Core Updates (ongoing): Broad quality assessments causing significant volatility Spam Updates (ongoing): Target various manipulative tactics
Long-Term Impact of Penalties
Even after recovery, penalties can leave lasting effects.
Trust deficit: Sites may struggle to regain full pre-penalty rankings Competitive losses: Lost time and rankings allowing competitors to advance Resource drain: Recovery efforts divert resources from growth initiatives Revenue impact: Traffic and conversion losses during penalty period Reputation damage: Known penalties affecting partnerships and opportunities
Conclusion
Search engine penalties negative ranking impacts from guideline violations or algorithm updates represent serious threats to organic visibility requiring immediate attention when detected. These enforcement mechanisms, whether manual actions applied by human reviewers or algorithmic demotions triggered by quality-detecting algorithms, can cause dramatic traffic losses ranging from partial ranking suppression to complete deindexing where entire sites vanish from search results.
Prevention through ethical SEO practices, quality content creation, natural link building, and technical compliance proves far easier than recovery from established penalties. When penalties occur, swift action identifying violations, implementing comprehensive fixes, and submitting reconsideration requests (for manual actions) or improving quality and waiting for algorithm refreshes (for algorithmic penalties) provides the path toward restoration.
The best penalty strategy is avoidance through conservative, user-focused optimization prioritizing genuine value over manipulation, quality over shortcuts, and sustainable practices over quick wins. When you build websites serving user needs through excellent content, ethical link acquisition, and technical compliance with search engine guidelines, you create penalty-resistant properties delivering lasting organic visibility without the catastrophic risks that manipulative tactics inevitably create when enforcement mechanisms detect and punish guideline violations.
Key Takeaways
- Penalties suppress rankings or deindex sites for guideline violations
- Manual actions require fixing issues and reconsideration requests
- Algorithmic penalties need quality improvements and algorithm refreshes
- Common causes include link schemes, thin content, and technical violations
- Traffic drops, Search Console warnings, and ranking losses indicate penalties
- Recovery requires identifying violations and implementing comprehensive fixes
- Prevention through ethical SEO far easier than recovery from penalties
- Quality content, natural links, and technical compliance prevent most penalties
- Not all ranking drops are penalties, many result from algorithm preference changes
- Long-term impacts can persist even after successful recovery efforts