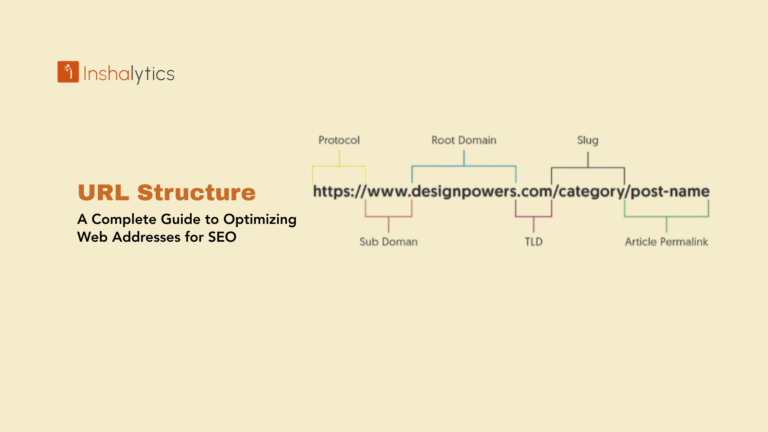
When a user types a query into Google, Bing, or any other search engine, the page they see next is called a Search Engine Results Page (SERP). The SERP is the core of how search engines deliver information, and understanding it is essential for effective digital marketing and SEO.
This glossary entry explains what a SERP is, how it works, its key components, the types of results shown, and why SERP features matter for your SEO strategy.
Navigate This Post
What Is a Search Engine Results Page (SERP)?
A Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is the page displayed by a search engine in response to a user’s query.
It contains a mix of organic results, paid ads, rich features, visuals, knowledge panels, and other elements designed to answer the user’s search intent as quickly and accurately as possible.
Every SERP is unique even if two people search the same keyword because results are influenced by:
- Location
- Search history
- Device type
- Language
- Personalization
- Algorithm variations
The modern SERP is no longer a list of ten blue links. It is an interactive results page filled with features designed to improve speed, accuracy, and user satisfaction.
Why SERPs Matter in Digital Marketing
For marketers and SEO professionals, SERPs are where visibility becomes reality.
Your position on the SERP directly affects:
- Click-through rates
- Organic traffic
- Brand awareness
- Lead generation
- Revenue growth
Understanding SERP structure helps you optimize content, compete effectively, and capture attention in a crowded digital landscape.
How SERPs Work: The Behind-the-Scenes Process
When a user enters a query, search engines go through several steps:
1. Crawling
Search engines discover content by scanning websites.
2. Indexing
Useful content is stored in the search engine’s database.
3. Ranking
Algorithms evaluate hundreds of signals to decide which pages best match the query.
4. Displaying Results
The SERP presents the best possible answers based on relevance, authority, intent, and quality.
This automated process happens in milliseconds.
Types of Results Shown on SERPs
SERPs contain a mixture of paid and organic results along with various interactive features.
1. Organic Results
These are the standard results earned through SEO rather than paid advertising.
Characteristics of organic results:
- Based on relevance + authority
- Not paid for
- Influenced by content quality, backlinks, technical SEO
- Can appear as traditional links or rich snippets
Organic visibility is the long-term goal of most SEO strategies.
2. Paid Results (Search Ads)
Paid ads appear above or below organic results. Marked with labels like “Sponsored” or “Ad,” they allow businesses to bid on keywords.
Benefits:
- Immediate visibility
- Highly targeted
- Useful for competitive niches
However, paid ads stop working when the budget ends unlike organic SEO.
Key SERP Features Every Marketer Should Know
Modern SERPs include multiple special features. These can drastically change click behavior, ranking opportunities, and content strategy.
Below are the most important SERP features:
1. Featured Snippet (Position Zero)
A highlighted answer box appearing at the top of the SERP.
It extracts the most relevant answer from a webpage.
Typical formats include:
- Paragraph answer
- List
- Table
- Steps
Featured snippets increase brand visibility and can drive high click-through rates.
2. Knowledge Panel
Appears on the right side (desktop) or top (mobile).
It includes information pulled from trusted sources such as:
- Knowledge Graph
- Wikipedia
- Official business profiles
Useful for branded searches, entities, celebrities, organizations, etc.
3. People Also Ask (PAA)
A section containing dropdown questions related to the original query.
These questions cover various search intents and help users explore deeper answers.
Optimizing content for PAA can significantly increase visibility.
4. Local Pack (Map Pack)
Displayed for local-intent searches such as:
- “Dentist near me”
- “Best café in Karachi”
- “SEO agency Lahore”
Includes:
- Map
- Three business listings
- Ratings
- Contact details
Critical for local SEO success.
5. Image Results
For visual-intent searches, Google shows a block of images directly on the SERP.
Optimizing images with alt text and relevant metadata helps content appear in image SERPs.
6. Video Results / Video Carousel
Often powered by YouTube, these appear for searches needing tutorials, reviews, or visual explanations.
Examples:
- “How to bake a cake”
- “Digital marketing tutorial”
Creating optimized video content increases chances of earning this real estate.
7. Top Stories (News Carousel)
Appears for trending, breaking, or news-related topics.
Ideal for publishers and authoritative news sources.
8. Shopping Results
Display product listings, prices, reviews, and merchant names.
These come from Google Merchant Center and paid ads.
9. Sitelinks
Displayed under a main result, showing important internal pages on a website.
Helps users navigate the site directly from the SERP.
10. Reviews & Star Ratings
SERPs may show star ratings and review counts from structured data markup.
These improve credibility and CTR.
The Importance of Search Intent in SERPs
Search engines prioritize the user’s purpose behind a query.
Understanding intent is essential for ranking on SERPs.
Main types of search intent:
1. Informational
User wants information.
Example: “What is SEO?”
2. Navigational
User wants a specific site.
Example: “Facebook login”
3. Transactional
User wants to buy something.
Example: “Best DSLR camera price”
4. Commercial Investigation
User is comparing options before buying.
Example: “Mailchimp vs HubSpot”
Content must match the exact intent to appear in relevant SERP features.
How SERPs Impact SEO Strategy
SERPs influence every stage of SEO planning.
Here’s how they shape your strategy:
1. Determine Content Format
If SERP shows videos → create video content.
If SERP shows listicles → structure content in lists.
2. Identify Ranking Difficulty
SERPs tell you whether you’re competing against:
- Brands
- Publishers
- Informational sites
- Forums
- E-commerce stores
This helps in selecting the right keywords.
3. Understand Keyword Intent
Analyzing the SERP reveals what users actually want, not just what they search.
4. Spot Opportunities to Win SERP Features
If PAA dominates → optimize FAQs.
If featured snippet exists → format content as a direct answer.
5. Improve CTR with Optimized Metadata
SERP appearance impacts how many users click your result.
Optimized titles + meta descriptions = higher CTR.
How LLMs (AI) Are Changing SERPs
Search engines now integrate AI features, and LLMs like Google’s SGE (Search Generative Experience) and third-party tools influence how users interact with information.
AI-driven SERPs show:
- Summarized answers
- Conversational responses
- Structured insights
- Links for deeper exploration
This means modern content must be:
- Factually accurate
- Well-structured
- Semantic-rich
- Skimmable
- Supported by expertise
Content optimized for LLMs has a greater chance of being included in AI summaries on SERPs.
Best Practices for SERP Optimization
To increase your chances of ranking and capturing SERP features:
✔ Understand search intent
✔ Optimize for featured snippets
✔ Use structured data/schema markup
✔ Improve website speed
✔ Create clear, concise answers
✔ Add FAQs to your content
✔ Use visuals (images, videos)
✔ Improve E-E-A-T signals
✔ Optimize metadata for clicks
✔ Update outdated content regularly
These actions help your pages gain visibility across multiple SERP features not just organic rankings.
Final Definition
A Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is the page a search engine displays after a user enters a query. It includes organic results, paid ads, and rich SERP features such as featured snippets, local packs, images, videos, and knowledge panels. Understanding SERP structure helps marketers optimize content, align with search intent, and improve visibility across multiple result types.