A search engine is a software system designed to search for information on the internet by scanning billions of web pages and returning the most relevant results for user queries. When you type a question or keyword into Google, Bing, Yahoo, or other search platforms, complex algorithms instantly analyze their massive databases (indexes) to present an ordered list of web pages, images, videos, and other content matching your search intent. Search engines serve as the primary gateway to information online, processing over 8.5 billion searches daily worldwide.
Search engines operate through three fundamental processes: crawling the web to discover content, indexing that content in organized databases, and ranking results based on relevance and quality when users perform searches. Understanding how search engines work is essential for digital marketing, SEO, and anyone seeking to increase online visibility or simply navigate the internet effectively.
Navigate This Post
Major Search Engines
Market Share: 91-93% globally (as of 2024)
The dominant search engine worldwide, Google processes over 8.5 billion searches daily. Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google revolutionized search with its PageRank algorithm that evaluated link quality. Today, Google uses sophisticated AI-powered algorithms considering hundreds of ranking factors.
Key Features:
- Knowledge Graph panels
- Featured snippets and AI Overviews
- Google Images, Videos, Maps, Shopping
- Personalized results based on location and history
- Voice search through Google Assistant
- Mobile-first indexing
Bing
Market Share: 3-4% globally, higher in the US (8-9%)
Microsoft’s search engine, launched in 2009, is the second-largest search engine globally. Bing powers searches for Microsoft Edge, Windows, and Amazon’s Alexa. It also provides search results for Yahoo and DuckDuckGo’s paid search.
Key Features:
- Visual search capabilities
- Rewards program for searching
- Integration with Microsoft products
- AI-enhanced results through Copilot
- Similar algorithmic principles to Google
Yahoo
Market Share: 1-2% globally
Once the internet’s most popular search portal, Yahoo now uses Bing’s search technology while maintaining its own interface. Yahoo remains relevant for email services, news, and finance content.
DuckDuckGo
Market Share: Less than 1%
Privacy-focused search engine that doesn’t track users or personalize results based on search history. Growing in popularity among privacy-conscious users.
Key Features:
- No user tracking or data collection
- No filter bubble from personalized results
- Anonymous searching
- Uses multiple sources including Bing
Baidu
Market Share: Dominant in China (60-70% in China)
China’s leading search engine, operating under Chinese internet regulations. Essential for businesses targeting Chinese markets.
Yandex
Market Share: Dominant in Russia (60%+ in Russia)
Russia’s largest search engine, offering search, maps, email, and other services tailored to Russian-speaking users.
Other Notable Search Engines
- Ecosia – Plants trees with ad revenue
- Brave Search – Privacy-focused with independent index
- Naver – Leading search engine in South Korea
- Seznam – Popular in Czech Republic
How Search Engines Work
Search engines follow a three-stage process to deliver relevant results in milliseconds.
1. Crawling (Discovery)
Search engines use automated programs called crawlers, spiders, or bots to discover and visit web pages across the internet.
The Crawling Process:
- Starting points – Crawlers begin with known URLs from previous crawls, sitemaps, and new submissions
- Following links – Bots follow hyperlinks from one page to another, discovering new content
- Re-crawling – Popular sites and frequently updated content are crawled more often
- Robots.txt compliance – Crawlers respect directives in robots.txt files about which pages to avoid
- Continuous process – Crawling happens constantly as the web grows and changes
Google’s Crawlers:
- Googlebot (desktop and mobile versions)
- Googlebot-Image (images)
- Googlebot-Video (videos)
- Googlebot-News (news content)
Factors Affecting Crawl Frequency:
- Page popularity and traffic
- Update frequency
- Site authority and trust
- Server speed and reliability
- Internal linking structure
- Crawl budget limitations
2. Indexing (Organization)
After crawling, search engines process and store information in massive databases called indexes.
The Indexing Process:
- Content analysis – Search engines analyze text, images, videos, and other media
- Keyword extraction – Identifying main topics, keywords, and themes
- Understanding context – Natural language processing determines meaning and intent
- Entity recognition – Identifying people, places, organizations, and concepts
- Relationship mapping – Understanding how pages connect and relate to each other
- Database storage – Organizing information for rapid retrieval
What Gets Indexed:
- Page content (text, headings, images)
- Meta tags (title, description)
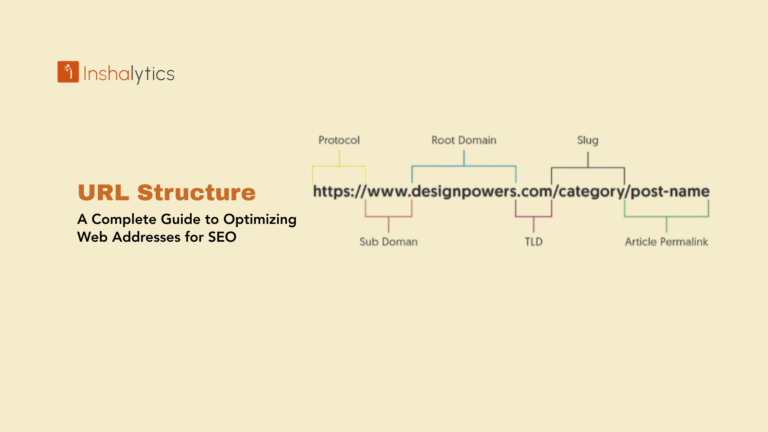
- URL structure
- Internal and external links
- Structured data markup
- Multimedia content
- Page load speed and mobile-friendliness
What Prevents Indexing:
- Noindex meta tags
- Robots.txt blocking
- Password-protected pages
- Duplicate content
- Low-quality or thin content
- Technical errors (404s, server errors)
3. Ranking (Relevance Determination)
When users search, algorithms evaluate indexed pages and return results ordered by relevance and quality.
Key Ranking Factors:
Content Relevance – How well page content matches the search query and satisfies user intent.
Content Quality – Depth, accuracy, originality, and expertise demonstrated in the content.
Backlinks – Number and quality of other websites linking to the page, signaling authority and trust.
User Experience – Page speed, mobile-friendliness, secure connection (HTTPS), and Core Web Vitals.
E-E-A-T – Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, especially for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content.
Freshness – How recently content was published or updated, particularly important for time-sensitive queries.
User Engagement – Click-through rates, dwell time, bounce rates, and pogo-sticking behavior.
Technical SEO – Proper site structure, crawlability, schema markup, and technical optimization.
Personalization – Location, search history, device type, and user preferences influence individual results.
Types of Search Results
Modern search engines display various result types beyond traditional organic listings.
Organic Results
Standard unpaid listings ranked by algorithmic relevance. These “10 blue links” remain the core of search results.
Paid Advertisements
Sponsored listings appearing above or below organic results, marked as “Ad” or “Sponsored.” Advertisers pay per click through platforms like Google Ads.
Featured Snippets
Position zero results appearing above organic listings, providing direct answers extracted from web pages. These include:
- Paragraph snippets
- List snippets
- Table snippets
- Video snippets
Knowledge Panels
Information boxes appearing on the right side (desktop) showing facts about entities like people, places, organizations, or concepts, sourced from Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Local Pack
Map-based results showing three local businesses for location-based queries, crucial for local SEO.
People Also Ask (PAA)
Expandable question boxes related to the search query, providing additional relevant questions and answers.
Image and Video Carousels
Visual content blocks displaying relevant images or videos for applicable queries.
Shopping Results
Product listings with images, prices, and merchant information for commercial queries.
News Results
Recent news articles for current events or trending topics.
AI Overviews (SGE)
Google’s AI-generated summaries synthesizing information from multiple sources, appearing at the top of results for certain queries.
How Search Engines Make Money
Pay-Per-Click Advertising
The primary revenue model for search engines. Advertisers bid on keywords, and their ads appear in search results. They pay only when users click their ads.
Google Ads (formerly AdWords) generates over 80% of Google’s revenue, making it one of the most profitable advertising platforms globally.
Display Advertising
Banner ads and display campaigns shown across search engine properties and partner networks.
Shopping Ads
Product listings in search results where retailers pay for placement and clicks.
Local Service Ads
Verified local business listings with pay-per-lead pricing models.
The Evolution of Search Engines
Early Days (1990s)
First search engines like Archie, Veronica, and WebCrawler used basic keyword matching. Yahoo began as a manually curated directory.
Google Era (Late 1990s-2000s)
Google’s PageRank revolutionized search by considering link quality. The algorithm wars began as Google dominated through superior relevance.
Algorithm Updates (2010s)
Major updates like Panda (content quality), Penguin (link quality), Hummingbird (semantic search), and RankBrain (machine learning) continuously refined results.
AI and Machine Learning (2020s)
BERT, MUM, and other AI models understand natural language and context at unprecedented levels. Search becomes more conversational and contextually aware.
Generative AI Era (2023+)
AI Overviews, conversational search, and LLM-powered results transform how users interact with search engines, potentially reducing traditional click-through patterns.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Understanding how search engines work enables website owners to optimize for better visibility.
Why SEO Matters:
- 68% of online experiences begin with search engines
- First organic result receives 28-40% of clicks
- 75% of users never scroll past the first page
- Organic search drives more traffic than social media and paid ads combined
Core SEO Principles:
- Create quality content that satisfies user intent comprehensively
- Optimize technical foundations (speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability)
- Build authoritative backlinks from reputable sources
- Improve user experience to keep visitors engaged
- Target relevant keywords users actually search for
- Stay updated on algorithm changes and best practices
The Future of Search Engines
AI-Powered Search
Artificial intelligence and large language models are transforming search from keyword matching to understanding complex queries and generating synthesized answers.
Voice and Visual Search
Voice assistants and image-based searches are growing, requiring new optimization strategies beyond traditional text-based SEO.
Personalization and Privacy
Balancing personalized results with privacy concerns shapes how search engines collect and use data.
Multi-Modal Search
Combining text, voice, image, and video inputs for more natural search experiences.
Zero-Click Searches
Featured snippets and AI overviews increasingly provide answers without users clicking through to websites, changing traffic patterns and SEO strategies.
Conclusion
Search engines are sophisticated software systems that have become indispensable infrastructure for the modern internet. By crawling billions of pages, organizing information in massive indexes, and ranking results based on complex algorithms, search engines like Google, Bing, and others serve as the primary gateway to online information for billions of users daily.
Understanding how search engines operate from the technical processes of crawling and indexing to the algorithmic factors determining rankings is essential for anyone involved in digital marketing, web development, or online business. As search technology evolves with artificial intelligence and changing user behaviors, the fundamental mission remains constant: connecting users with the most relevant, trustworthy, and useful information as quickly as possible.
Whether you’re optimizing a website, running paid campaigns, or simply searching for information, recognizing how search engines work helps you leverage their power effectively and navigate the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Key Takeaway: A search engine is a software system that searches the internet by crawling billions of web pages, indexing content in organized databases, and ranking results based on relevance and quality algorithms. Major search engines like Google (91% market share), Bing, and Yahoo process billions of daily searches, serving as the internet’s primary information gateway. Understanding search engine mechanics crawling, indexing, and ranking is essential for effective SEO, digital marketing, and online visibility.